| A Study of the Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Dreaming |
| M. Jouvet and D. Jouvet Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1963 Suppl. 24 |
| TABLE OF CONTENTS |
| Part 1 |
| Part 2 |
| Figures |
| Printable version |
Fig. 1 : The two phases of sleep in an intact cat
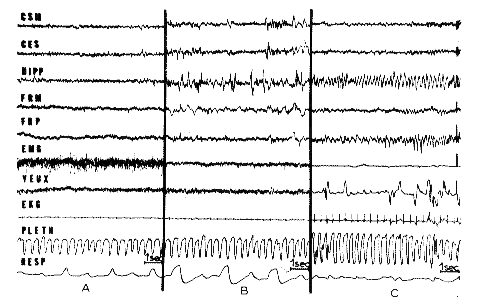
- A. Arousal: Fast cortical, hippocampal and reticular activity
- B. "Slow Sleep": Slow waves and spindles at the cortical and reticular level, persistence of EMG activity of the neck muscles (EMG).
- C. Rhombencephalic Phase of Sleep (RPS): Fast cortical and mesencephalic reticular activity similar to the arousal. Theta rhythm at the hippocampus (Hipp). Theta rhythm and spindles at the pontine reticular level. Total disappearance of the EMG activity. Rapid eye movements (Yeux). Augmentation of the plethysmographic index of the anterior leg. Irregularity of the respiration.
- CSM: Sensorimotor cortex;
- CES: Ecto-sylvian cortex;
- HIPP: Ventral hippocampus;
- FRM: Mesen cephalic reticular formation;
- FRP: Pontine reticular formation;
- EMG: Electromyogram from neck muscles;
- Yeux: Ocular movements;
- EKG: Electrocardiogram;
- Pleth: Plethysmogram of a leg;
- Resp: Respiratory movements.
From Jouvet (1962), with kind permission of Arch. Ital. Biol. (full-text)