| A Study of the Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Dreaming |
| M. Jouvet and D. Jouvet Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1963 Suppl. 24 |
| TABLE OF CONTENTS |
| Part 1 |
| Part 2 |
| Figures |
| Printable version |
Fig. 2 : RPS in a neodecorticate cat
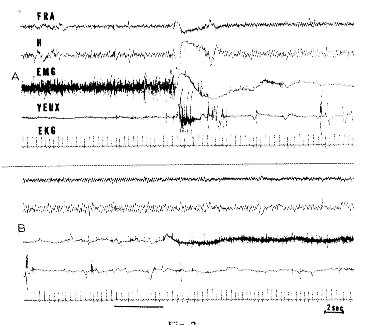
A. A theta rhythm appears at the level of the ventral hippocampus (H) and of the medial ventral reticular formation (FRA). At the same time, the EMG of the neck muscles disappears and rapid eye movements occur with some blinking. B. 40 sec after A: A very loud noise (horizontal line) arouses the cat. Scale: 2 sec.