| Telencephalic and rhombencephalic sleep in the cat |
| Jouvet M. The Nature of Sleep Ciba Foundation Symposium Churchill (1961) |
| TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|
Topography of the systems responsible for the two stages of sleep |
| Figures |
| Printable version |
Figure 2
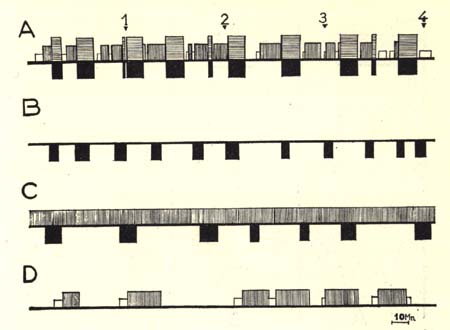
Diagrammatic representation of the sleep-wakefulness rhythm in
- (A) intact,
- (B) decorticate,
- (C) mesencephalic cats, and
- (D) cats with medial coagulation of the pontine reticular formation.
Four hours continuous recording, one week after the intervention, for each cat.
(Time scale: 10 minutes)
In black, the rhombencephalic stage of sleep with fast cortical EEG pattern in normal cats (horizontal hatching) and spindling activity at the pontine level, total disappearance of EMG activity (movements of eyes, etc.) in normal, decorticate and mesencephalic cats.
In white, spindling activity on the cortex.
Vertical hatching, slow wave and spindles at the cortical and diencephalic level.
Horizontal line, arousal.
Note the absence of the slow wave and spindle phase of sleep in de corticate cat, and the absence of the rhombencephalic phase in cat with pontine lesion. Note also the relative wakefulness of the latter type of preparation.